In our increasingly interconnected world, the health of humans, animals, and the environment are inextricably linked. This realization has given rise to the One Health approach, a transformative strategy that seeks to optimize health outcomes by integrating these interconnected domains to one ecosystem. As we face complex global health challenges like pandemics, the One Health perspective offers a crucial framework for addressing these multifaceted issues.
Understanding One Health
One Health is defined by the One Health High-Level Expert Panel as “an integrated, unifying approach that aims to sustainably balance and optimize the health of people, animals, and ecosystems.” This approach recognizes that the health of humans, domestic and wild animals, plants, and the wider environment are closely linked and interdependent.
The need for a One Health approach has become increasingly apparent in recent years. Consider these sobering statistics:
- In the last three decades, over 30 new human pathogens have been detected, 75% of which originated in animals.
- Since 2003, the world has seen over 15 million human deaths and US$ 4 trillion in economic losses due to diseases and pandemics related to One Health threats.
- Each year, environmental factors claim the lives of approximately 13 million people. Changing weather patterns are spreading diseases, and extreme weather events increase fatalities, straining healthcare systems to keep up.
One Health broadens the moral circle and redefines our relationships with other humans, animals, and the environment to successfully optimize the health of the planet and its diverse inhabitants.
Key Areas of Focus
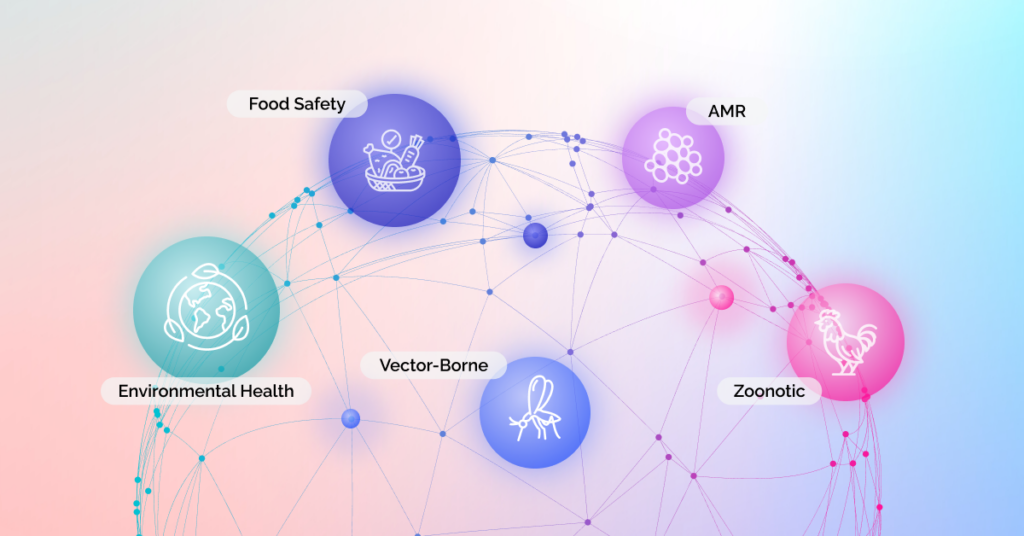
The One Health approach applies to a wide range of critical health issues:
- Zoonotic Diseases: Infections that can be transmitted between animals and humans, such as COVID-19, Ebola, and avian influenza.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): The ability of microorganisms to resist antimicrobial treatments, posing a significant threat to global health.
- Food Safety and Security: Ensuring a safe and sustainable food supply from farm to table.
- Vector-Borne Diseases: Illnesses transmitted by vectors like mosquitoes and ticks, including malaria, dengue fever, and Lyme disease.
- Environmental Health – Tackling issues like water, soil, and air pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change, that affect both human and animal health.
It’s crucial to recognize that climate change is an integral part of a cycle that both impacts and is impacted by global health.
The Importance of Collaboration
A key principle of the One Health approach is cross-sector collaboration. Effective implementation requires cooperation between diverse fields including human medicine, veterinary medicine, environmental science, agriculture, and public health. This multidisciplinary approach enables more comprehensive surveillance, research, and intervention strategies.
The Significance of Prevention
Equally important is the emphasis on a preventive attitude, which includes vigilant surveillance and monitoring of potential health threats. Proactive measures are essential to identifying and mitigating risks before they escalate. Laboratories play a crucial role in this preventive framework by providing accurate and timely diagnostics, facilitating early detection of diseases, and supporting ongoing monitoring efforts. Their contributions are vital to ensuring a swift response to emerging health issues, thereby safeguarding the health of humans, animals, and the environment.
Global Initiatives and Regulatory Support
Recognizing the importance of One Health, major global health organizations, and regulatory bodies are increasingly incorporating this approach into their frameworks:
- The World Health Organization (WHO), Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE), and United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) have formed a One Health Quadripartite, developing a joint plan of action.
- The European Commission has adopted guidelines on the prudent use of antimicrobials in both human and animal health and is working towards integrated surveillance and prevention of zoonotic spillovers.
- The EU’s Pharmaceutical package, adopted in April 2023, includes a proposal for a Council Recommendation on AMR with measures across human health, animal health, and the environment.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Despite its potential, implementing One Health faces several challenges:
- Data Integration: Developing comprehensive databases and resources to support information sharing across sectors.
- Capacity Building: Mapping existing initiatives and building the next generation One Health workforce.
- Surveillance: Creating an integrated One Health surveillance system to monitor risks and identify patterns across human, animal, and environmental health.
- Coordination: Establishing mechanisms for routine and emergency coordination among relevant stakeholders.
- Understanding Drivers: Gaining a more complete understanding of the factors driving zoonotic disease spillover and emergence.
As we move forward, addressing these challenges will be crucial to fully realizing the benefits of the One Health approach. By fostering collaboration, investing in research and surveillance, and developing comprehensive policies, we can create a more resilient and sustainable global health system.
Briya’s Role in Advancing One Health
Briya, a leading medical data retrieval network, plays a pivotal role in supporting the One Health approach through its innovative data solutions. By facilitating real-time access to high-quality, comprehensive data, Briya enables researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers to make informed decisions that encompass the full spectrum of health determinants.
- Data Integration: Briya’s platform integrates data from various sources, including medical records, environmental data, and veterinary information. This holistic view allows for a better understanding of the connections between human, animal, and environmental health.
- Collaborative Research: Briya empowers hospitals and research institutions to participate in global collaborative research. This fosters interdisciplinary studies that are essential for tackling complex One Health issues.
- AI and Data Analytics: By leveraging artificial intelligence and advanced data analytics, Briya helps identify patterns and trends across different health domains. This can lead to better understanding of environmental health impacts and the development of primary prevention strategies as well as early detection of disease outbreaks (secondary prevention), leading to effective interventions and response.
Conclusion
The One Health approach is indispensable for addressing the multifaceted health challenges of our time. By promoting a collaborative and integrative perspective, we can achieve significant advancements in public health, animal health, and environmental sustainability. Briya’s cutting-edge data solutions are instrumental in this effort, providing the tools and insights needed to drive impactful research and informed decision-making. Together, we can build a healthier, more sustainable, and morally grounded future for everyone.
Sources:
One Health: A new definition for a sustainable and healthy future